- 🤔 Introduction: Are You Wondering Which Siding Keeps Homes Warmer?
- 📑 Why Insulation Matters in Siding
- 🧱 What Is Composite Siding?
- What Is Vinyl Siding?
- 📊 Direct Comparison: Composite vs. Vinyl Siding
- 🔍 Insulation Performance: Which Wins?
- 🌡️ Energy Efficiency in Real Homes
- 🛠️ Installation Differences That Affect Insulation
- 💲 Cost vs. Insulation Value
- 🌍 Environmental Impact and Insulation
- 👤 Which Siding Is Best for Your Climate?
- ⭐ Final Verdict: Which Offers Better Insulation?
- 📊 Quick Reference: Siding and Insulation Performance
- 📝 Conclusion
🤔 Introduction: Are You Wondering Which Siding Keeps Homes Warmer?
Have you ever stepped into your home on a freezing day and felt the cold seeping through the walls? I know that frustration well. Many homeowners spend thousands of dollars on siding only to find their energy bills climbing and their comfort dropping. That’s when the question hits: Does composite siding insulate better than vinyl siding?
This is not just about looks. Your siding is your home’s shield, keeping heat inside during winter and blocking heat during summer. If you’re starting a remodel or new build, understanding the insulation power of each siding material will save you money and stress for years.
For expert guidance on siding, roofing, and insulation solutions, visit 👉 Akron Roofing Experts.
📑 Why Insulation Matters in Siding
Siding is more than curb appeal. It plays a direct role in energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and long-term savings. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, properly insulated siding can reduce household energy use by up to 20% annually. Poor insulation, however, forces HVAC systems to work harder, leading to higher utility costs.
Insulation performance is measured using the R-value, which shows how well a material resists heat transfer. A higher R-value means better insulation. Let’s see how composite siding and vinyl siding compare.
🧱 What Is Composite Siding?
Composite siding is a modern siding option made from a blend of wood fibers, resins, and polymers. It’s engineered for durability, energy efficiency, and weather resistance.
Key Features of Composite Siding 📄
- Strong resistance to moisture and pests.
- Designed with insulating cores that boost R-value.
- Mimics the look of real wood but with less maintenance.
- Average lifespan: 30–50 years.
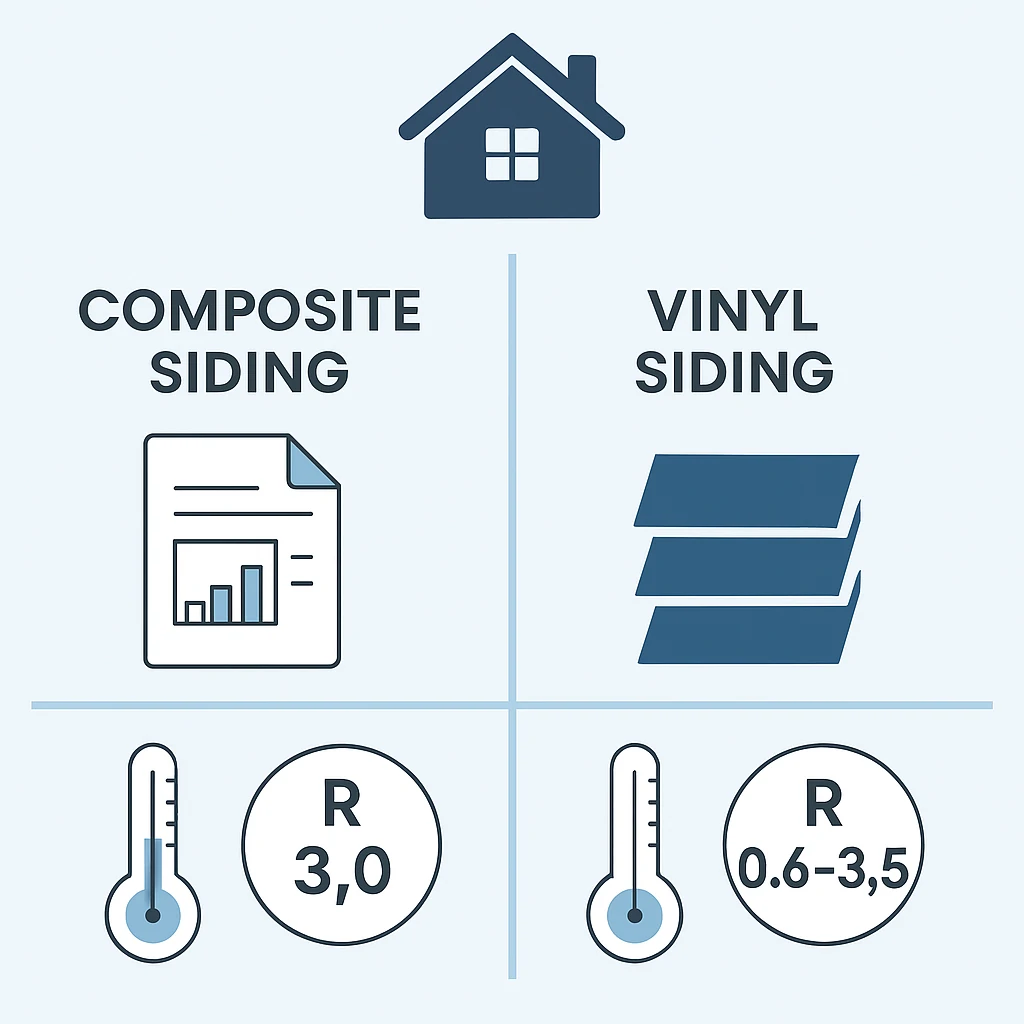
📌 Fact: Composite siding panels often reach an R-value between 0.8 and 3.0, depending on thickness and brand.
What Is Vinyl Siding?
Vinyl siding, introduced in the 1950s, remains the most widely used siding in the U.S. It is made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and is popular for affordability and low maintenance.
Key Features of Vinyl Siding 📄
- Lightweight and quick to install.
- Available in many colors and styles.
- Resistant to rot and insects.
- Average lifespan: 20–40 years.
📌 Fact: Standard hollow vinyl siding has a low R-value of 0.61, though insulated vinyl siding (with foam backing) can reach R-values of 2.0–3.5.
📊 Direct Comparison: Composite vs. Vinyl Siding
| Feature | Composite Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Wood fibers + resin + polymers | PVC (polyvinyl chloride) |
| Average R-Value | 0.8 – 3.0 | 0.61 (hollow) / 2.0 – 3.5 (insulated) |
| Durability | 30–50 years | 20–40 years |
| Moisture Resistance | High | High |
| Maintenance | Low, occasional cleaning | Very low, easy cleaning |
| Cost Range | $7–$15 per sq. ft. installed | $4–$12 per sq. ft. installed |
| Appearance | Realistic wood-like finish | Wide color selection |
🔍 Insulation Performance: Which Wins?
When comparing insulation, insulated vinyl siding and composite siding often overlap. Composite siding naturally resists heat transfer due to its engineered core. Insulated vinyl siding relies on a foam backing that enhances its R-value.
How They Compare:
- Composite siding: Consistently performs better than hollow vinyl siding, offering stronger thermal protection.
- Insulated vinyl siding: Matches or sometimes exceeds composite siding in R-value, but costs can rise with premium options.
📌 Fact: According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Housing Survey, homes with insulated siding see up to 12% lower annual energy costs compared to homes with non-insulated siding.
🌡️ Energy Efficiency in Real Homes
Imagine two identical homes in a cold climate:
- 🏠 Home A with composite siding has an R-value of 2.5.
- 🏠 Home B with hollow vinyl siding has an R-value of 0.61.
Over one year, Home A reduces heating energy use by up to 15%, while Home B struggles to keep warm air inside.
If Home B upgrades to insulated vinyl siding with an R-value of 3.0, it surpasses Home A in thermal performance, proving that insulation choice matters as much as material.
🛠️ Installation Differences That Affect Insulation
Even the best siding fails if it’s poorly installed.
- Composite siding requires precise fitting and sealing. Gaps can reduce its insulation power.
- Vinyl siding must allow for expansion and contraction. Improper nailing can lead to warping and drafts.
💡 Pro Tip: Always hire certified installers to maximize insulation benefits. For professional siding help, visit 👉 Akron Roofing Experts.
💲 Cost vs. Insulation Value
Cost plays a big role in decision-making.
| Siding Type | Average Installed Cost per Sq. Ft. | Insulation Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Composite Siding | $7–$15 | High, built-in insulation |
| Hollow Vinyl Siding | $4–$8 | Low, minimal insulation |
| Insulated Vinyl | $8–$12 | High, foam backing adds strong R-value |
📌 While composite siding has a higher upfront cost, its longer lifespan and insulation performance balance the investment.
🌍 Environmental Impact and Insulation
Siding choice affects sustainability:
- Composite siding uses recycled wood fibers and resins, offering eco-friendly durability.
- Vinyl siding is petroleum-based but recyclable in some regions.
- Insulated siding reduces energy waste, lowering your carbon footprint.
📌 Fact: The U.S. Green Building Council states that homes with high-efficiency siding reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 10% annually.
👤 Which Siding Is Best for Your Climate?
- ❄️ Cold Climates: Composite siding or insulated vinyl both provide strong thermal barriers.
- ☀️ Hot Climates: Vinyl siding resists heat absorption, but insulated versions keep interiors cooler.
- 🌧️ Humid Regions: Composite siding resists swelling and rotting better than wood siding, while vinyl remains immune to mold.
⭐ Final Verdict: Which Offers Better Insulation?
If comparing basic vinyl siding vs composite siding, composite wins on insulation. But when upgraded to insulated vinyl siding, the difference narrows or even flips in favor of vinyl.
- Choose composite siding if you want a balance of insulation, durability, and wood-like beauty.
- Choose insulated vinyl siding if you want maximum insulation at a slightly lower cost.
For personalized advice, contact 👉 Akron Roofing Experts.
📊 Quick Reference: Siding and Insulation Performance
| Factor | Composite Siding | Vinyl Siding (Insulated) |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value Range | 0.8 – 3.0 | 2.0 – 3.5 |
| Best Use | Cold & variable climates | Cold, hot, or mixed climates |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront, strong ROI | Mid-range, strong ROI |
| Lifespan | 30–50 years | 20–40 years |
📝 Conclusion
When choosing between composite siding and vinyl siding, focus on insulation performance, cost, and climate. Composite siding offers natural strength and good insulation, while insulated vinyl siding provides impressive R-values at a competitive cost. The best choice depends on your home’s location, design goals, and budget.
For expert siding solutions and insulation guidance, visit 👉 Akron Roofing Experts.